Water vapor is a fascinating phenomenon of nature. It is the gaseous form of water that we can see and feel when we step outside on a humid day. But what is the process of water vapor turning into liquid? This question is one of the most interesting and important questions in the study of science and the environment.
To understand the process of water vapor becoming a liquid, it is important to understand the fundamentals of the water cycle. The water cycle is the process by which water is continuously cycled through the atmosphere and back to the Earth’s surface and bodies of water. This cycle is driven by energy from the sun and other factors such as temperature and pressure. As water is heated by the sun, it evaporates into the atmosphere as water vapor. But how does this water vapor turn back into liquid water? That is the question we shall explore in this article.
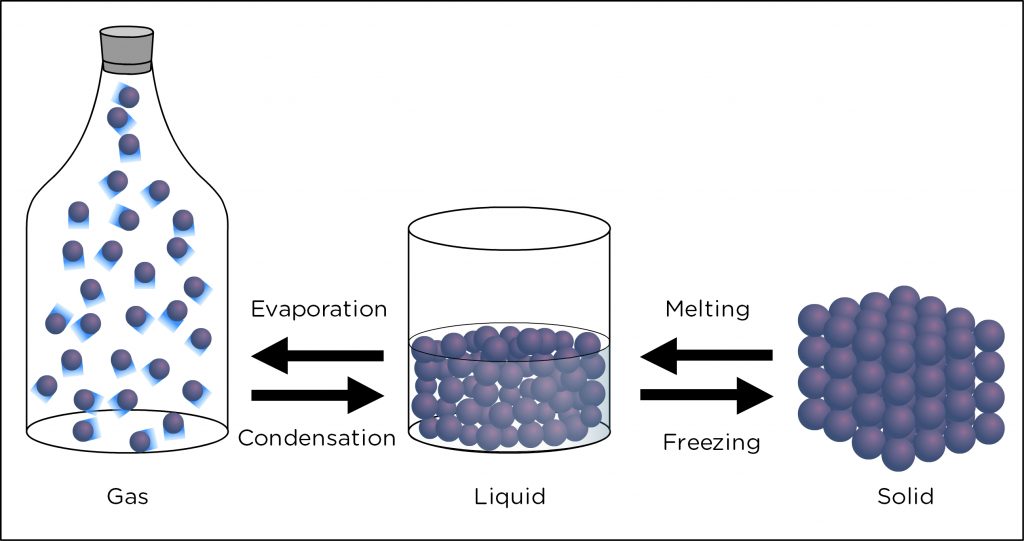
What is the Process of Water Vapor Becoming a Liquid?
Water vapor is a form of water that is present in the atmosphere as a gas. When the atmospheric temperature and pressure conditions are favorable, water vapor can become a liquid. This process is known as condensation and is responsible for the formation of clouds, fog, and rain. In this article, we will discuss the process of water vapor becoming a liquid.
Cooling of the Air
When air is cooled, its capacity to hold moisture decreases. As the air cools, it is unable to hold as much water vapor and the vapor begins to condense and form droplets. This process is known as adiabatic cooling. As the air cools, the relative humidity of the air increases, meaning that the air is now able to hold more water vapor. When the relative humidity of the air reaches 100%, the air is said to be saturated and any additional water vapor will condense and form droplets.
The cooling of the air can be caused by a variety of factors such as the adiabatic expansion of air as it rises in the atmosphere, contact with a cold surface such as a mountain or a body of water, or the presence of particles such as dust or salt in the air that absorb heat.
Formation of Condensation Nuclei
The formation of condensation nuclei is a necessary step in the process of water vapor becoming a liquid. Condensation nuclei are tiny particles in the air that attract and hold water vapor. These particles can be of organic or inorganic origin, such as dust, soot, pollen, or salt. When the relative humidity of the air reaches 100%, the tiny water droplets form around these particles and become visible as fog, clouds, or rain.
The number of condensation nuclei in the air is affected by air pollution, as certain pollutants such as soot, dust, and pollen can act as condensation nuclei. In highly polluted areas, the number of condensation nuclei is increased, resulting in more frequent and intense precipitation.
Formation of Clouds
Once the air has become saturated, the droplets of water vapor that have formed around the condensation nuclei begin to grow and coalesce, forming clouds. Clouds can form at any altitude in the atmosphere, depending on the temperature and pressure of the air. As the clouds grow, the droplets of water vapor become heavier and eventually fall from the sky as rain or snow.
The type of clouds that form in the sky depends on the temperature of the air. Warmer air can hold more water vapor and therefore form higher clouds. Conversely, cooler air can form lower clouds. The clouds that form can also vary in shape and color, depending on the amount of moisture and the type of condensation nuclei present in the air.
Formation of Rain
The droplets of water vapor that make up clouds eventually become too heavy and fall from the sky as rain. The rate at which the droplets fall is determined by the size of the droplets and the speed at which they are falling due to the pull of gravity.
The formation of rain is also affected by the temperature of the air. Colder air can hold less water vapor and therefore produces smaller rain droplets. Conversely, warmer air can hold more water vapor and produces larger and heavier rain droplets.
Formation of Fog
Fog is a form of precipitation that occurs when the air is cooled to the point where the moisture in the air condenses and forms tiny droplets. Fog can form at any altitude in the atmosphere and is usually visible at ground level.
Fog can form when the air is cooled by contact with a cold surface, usually a body of water. The fog forms when the air near the surface is cooled to the dew point and the moisture in the air condenses and forms droplets. Fog can also form when the air is cooled by adiabatic cooling, such as when air rises in the atmosphere, cools, and the moisture in the air condenses and forms droplets.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Process of Water Vapor Becoming a Liquid
The process of water vapor becoming a liquid is a fundamental component of the global water cycle. It is a natural way of recycling moisture from the atmosphere into the environment. This article will address some common questions about the process.
What is the Process of Water Vapor Becoming a Liquid?
The process of water vapor becoming a liquid is known as condensation. It occurs when water molecules in the atmosphere cool down to their dew point temperature. When the molecules reach their dew point, they become heavy enough to form droplets that eventually become a liquid. This liquid can then fall to the ground as precipitation.
What Factors Affect the Process of Water Vapor Becoming a Liquid?
The process of water vapor becoming a liquid is primarily influenced by temperature, pressure, and humidity. Warmer air is able to hold more water vapor than colder air, so as temperatures drop the water vapor condenses into droplets. Additionally, atmospheric pressure affects the ability of the air to hold water vapor. When the pressure is higher, the air has a harder time retaining water vapor, and more condensation occurs. The amount of water vapor in the air, known as the relative humidity, also affects the process. The higher the relative humidity, the more water vapor is in the atmosphere, and the greater the likelihood of condensation.
What Conditions are Ideal for Water Vapor Becoming a Liquid?
For the process of water vapor becoming a liquid to occur, the air must be saturated with water vapor and the dew point temperature must be reached. This usually happens when the air is very humid and the temperature is cool. This is why condensation is often seen on cold surfaces like windows, and why the air often feels damp and humid in the morning.
What is the Difference Between Condensation and Evaporation?
Condensation and evaporation are opposite processes of the same cycle. Condensation is when water vapor becomes a liquid, while evaporation is when a liquid becomes a gas. As water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the environment, which cools the surrounding air. This process is the opposite of condensation, where water vapor cools and becomes a liquid.
What are Some Examples of Condensation in Nature?
Condensation is a key part of the global water cycle, and there are a number of examples of it happening in nature. Fog is one of the most common examples of condensation in nature. Fog is formed when water vapor in the air condenses into tiny droplets, which can then form a thick layer of fog. Dew is another example of condensation, and it forms when water vapor condenses on cold surfaces, often in the early morning hours.

Water evaporation experiment
The process of water vapor becoming a liquid is an important part of the water cycle. Water vapor is constantly being evaporated from the surface of bodies of water, and then condensing and becoming liquid again. This process is essential for keeping the water cycle in balance, and ensures that the Earth has an adequate supply of water for all its inhabitants.
Without water vapor becoming a liquid, the Earth’s climate and its habitats would drastically change. It is an important part of the cycle of life, and one that is often taken for granted. Understanding the process of water vapor becoming a liquid helps to remind us of the importance of conserving our water resources and protecting the environment.
