Separating oil from water is a key process in many industries, from food production to environmental conservation, and can be achieved through a variety of chemical means. Understanding the principles of chemistry behind this process is crucial for anyone who wants to have the highest possible success rate. This article will examine how to separate oil from water using chemistry, and explain the importance of this process.
Chemistry is all around us and plays an integral role in the environment. In the case of separating oil from water, chemistry can be used to create a safe and efficient solution for a variety of purposes. Through careful manipulation of chemical reactions, it is possible to separate oil from water into two distinct phases, allowing for the safe disposal of the oil. This article will discuss the various types of separation techniques, the importance of understanding the chemistry involved, and provide tips on how to ensure the most successful outcome.
Oil and water can be separated using a process called decantation. This involves pouring the mixture into a container and allowing the oil to float to the top. Then, the oil can be skimmed off the surface and the water underneath can be removed. The oil can then be further separated from the water using distillation or adsorption.
The distillation technique involves heating the mixture until the oil boils and separates from the water. The oil vapor is then collected and condensed into liquid form. Adsorption is a process where the oil is absorbed onto a solid material. This material can then be removed from the mixture, leaving the water behind.
How to Separate Oil From Water Chemistry
Oil and water don’t mix, but they can be separated using various chemical methods. Separating oil from water is an important process in many industries, such as the food, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries. In this article, we’ll explain the chemistry behind separating oil from water, and discuss some of the most common methods used to do so.
Surface Tension and Surface Active Agents
Oil and water don’t mix because of the differences in their molecular structures. Water molecules are polar, meaning that the oxygen atom in the molecule has a slightly negative charge, while the hydrogen atoms have slightly positive charges. Oil molecules, on the other hand, are non-polar and have no charge. This means that oil molecules can’t form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, so the two don’t mix.
The process of separating oil and water is aided by surface tension. Surface tension is the phenomenon wherein the surface of a liquid behaves as if it were a thin elastic sheet. This means that when oil and water come into contact with each other, the water molecules will form a layer on top of the oil, allowing the two to be easily separated. This phenomenon can be further enhanced by adding a surface active agent, such as a surfactant, to the mixture.
Gravity Separation
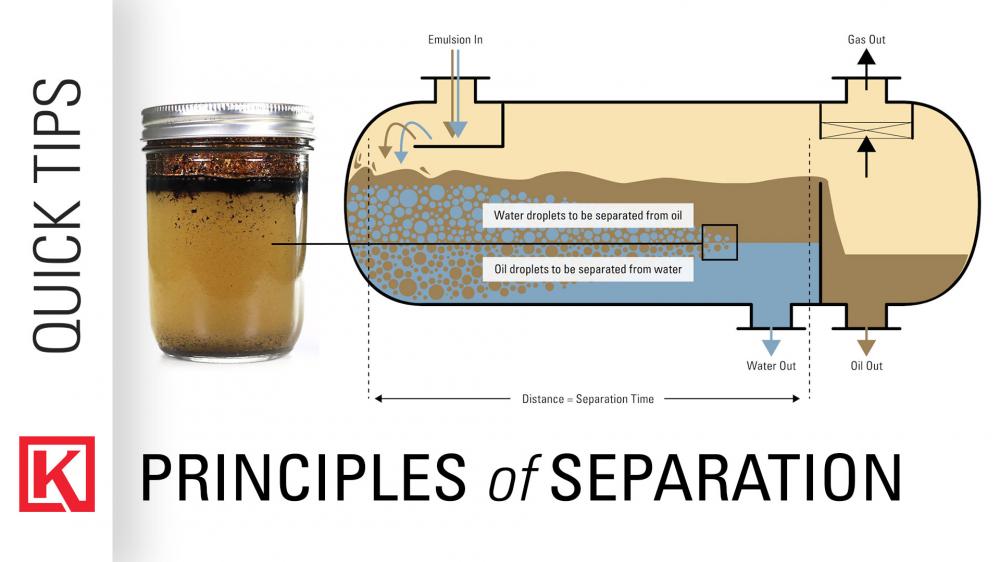
Gravity separation is one of the most common methods used to separate oil and water. This method relies on the fact that oil is less dense than water. When the two are mixed, the oil will float to the top of the water, allowing it to be skimmed off. This process is often used in oil spill clean-up operations, as it is relatively simple and inexpensive.
Gravity separation can also be used in combination with other methods, such as adsorption. Adsorption is the process by which a substance adheres to the surface of another substance. In this case, adsorbent materials are added to the oil-water mixture, which allows the oil to adhere to their surfaces. This makes it easier to separate the oil from the water, as it can be skimmed off the surface of the adsorbent material.
Centrifugation
Centrifugation is another common method used to separate oil from water. In this method, the oil-water mixture is placed in a spinning centrifuge. The spinning motion causes the oil and water to separate, with the oil being forced to the outside of the centrifuge, and the water being forced to the center. This method is often used in industrial applications, as it is very efficient and can be used to separate large quantities of oil and water.
Centrifugation can also be used in combination with other separation methods, such as adsorption. In this case, the oil is adsorbed onto the surface of an adsorbent material, which is then placed in the centrifuge. This allows the oil and water to be more easily separated, as the adsorbent material collects the oil, while the water remains in the center of the centrifuge.
Membrane Separation
Membrane separation is another method used to separate oil and water. This method relies on the fact that oil molecules are larger than water molecules. A membrane is used to filter the oil-water mixture, allowing only the smaller water molecules to pass through, while the larger oil molecules are retained on the other side. This method is often used in the food and pharmaceutical industries, as it is very efficient and can be used to separate large quantities of oil and water.
Membrane separation can also be used in combination with other separation methods, such as adsorption. In this case, the oil is adsorbed onto the surface of an adsorbent material, and then passed through the membrane. This allows the oil and water to be more easily separated, as the adsorbent material collects the oil, while the water is filtered out by the membrane.
Frequently Asked Questions
Oil and water are immiscible substances, meaning that they don’t mix together. As a result, separating oil from water is an important process in many industries. In this article, we’ll look at the chemistry behind separating oil from water.
What is the Basic Process for Separating Oil from Water?
The basic process for separating oil from water involves two steps: first, the oil and water are allowed to settle, which causes them to separate into two distinct layers. This is known as “gravity separation.” Once the oil and water have separated, the oil can be removed from the surface of the water.
The second step involves using a number of chemical processes to further separate the oil from the water. This may involve using an emulsifier, which helps to break up large oil droplets and make them easier to separate. Other chemical processes, such as reverse osmosis, can also be used to remove oil from water.
What Factors Affect the Separation of Oil and Water?
The efficiency of the oil-water separation process is affected by a number of factors. The viscosity of the oil plays an important role, as thicker oils are more difficult to separate from water than thinner oils. The temperature of the water can also have an effect, as warmer water can reduce the surface tension of oil droplets, making them easier to separate from the water.
The pH of the water can also affect the separation process. Water with a higher pH can help to break up oil droplets, making them easier to separate. Additionally, the presence of other substances in the water, such as surfactants, can affect the separation process.
What are the Benefits of Separating Oil and Water?
The primary benefit of separating oil and water is that it allows the two substances to be reused. For example, the oil can be collected and used for fuel, while the water can be treated and recycled for use in other applications. Additionally, separating oil from water helps to protect the environment, as it prevents the oil from contaminating other bodies of water.
What are the Drawbacks of Separating Oil and Water?
The primary drawback of separating oil and water is that it can be a time-consuming and expensive process. Additionally, some of the chemical processes used to separate oil and water can be hazardous, and proper safety protocols must be followed when dealing with these chemicals. Finally, the separated oil and water must be disposed of properly, as improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination.
What are Some Common Applications of Oil-Water Separation?
Oil-water separation is used in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, wastewater treatment, and food processing. In the oil and gas industry, it is used to separate crude oil from wastewater produced during the extraction process. In wastewater treatment, it is used to separate oil from industrial wastewater, such as that produced by factories and refineries. Finally, in the food processing industry, it is used to separate oil from other food products.

Separtion of a mixture of oil and water using separating funnel
In conclusion, separating oil from water chemistry can be a complex process, but with the right knowledge and understanding of the process, it can be done in a safe and efficient way. Separating oil from water is an important step in many industrial processes, and knowing the right techniques can help ensure safety and efficiency when separating the two substances.
By understanding the fundamentals of oil-water chemistry, learning the right techniques, and having the right equipment, you can successfully separate oil from water in order to process it for a variety of applications. With this knowledge, you can guarantee that your process is safe and efficient.
